SEO and Search in Pre-AI era
Before the rise of AI-generated content, the user experience on search engines was centered around click-through results. When a user typed in a query, they were presented with a list of blue links, webpages ranked based on their relevance as determined by SEO signals like keywords, backlinks, and on-page optimization.
To increase visibility, especially in competitive niches, businesses heavily invested in SEO strategies and Search Engine Marketing (SEM).
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Companies invested in content marketing, technical SEO, backlink-building, and keyword optimization to climb Google’s rankings organically. The goal was to appear on the first page of search results; ideally in the top three positions which capture the vast majority of clicks.
- Paid Keywords (PPC – Pay-Per-Click): Businesses could bid on specific keywords through platforms like Google Ads. The goal was to have their result appear at the top of the page, clearly labeled as an ad, with a commission fee incurred each time someone clicked on it.
This ecosystem functioned on the assumption that users would click, either on organic links or paid ads, and that this traffic would be converted into sales, newsletter signups, or engagement.
In this model, answers lived on websites, and traffic was everything. Brands had to compete for visibility through optimized metadata, targeted content, and domain authority. The role of search engines was to direct users toward sources of information, not to provide it themselves.
But AI is changing that equation.
The arrival of AI and of the age of 0-click
The arrival of AI, specifically of ChatGPT in 2022, revolutionized the way users are searching information as well as how they interact with them. 2.5 billion prompts are sent daily on ChatGPT by its users. In comparison, 14 billion searches are made on Google daily. Despite search engines still being mostly used, more and more people are turning to AI for their searches.
There is a switch in the traditional search behavior. People are now using AI instead of search engines as AI directly provides informations (ie. ChatGPT gives you a list of restaurant recommendations in a certain area, users don’t have to search for it on Google Maps). They don’t need to click on any links or visit websites. This is 0-click.
Google recently launched Google AI, which consists of generating an AI summary before showing the links. This new feature is directly competing with ChatGPT, but is also pushing users who encounter Google AI not to visit any websites. Users are most likely to end their browsing session after visiting a search page with an AI summary. This new way of browsing results in a drop of clicks-through rates.
The main goal of Artificial Intelligence Search Engine Optimization (SAIO) is to integrate machine learning, natural language processing and large language models into the different strategies of search optimization. With Microsoft 365 Copilot or Google AI, we can see a shift in the way AI is integrated into various platforms to offer faster but also more relevant and personalized answers. This could be the beginning of the integration of AI in all kinds of businesses as it could become one of their ways of being closer with the customer.
What does it mean for the future of Google search ?
This new way of pairing AI with traditional search engines raises questions as well as concerns for the future of websites, businesses and user’s habits.
This evolution of AI and its bigger presence in our daily lives will have an impact on the businesses and their way of functioning. We could think that a shift could occur in the business model as they would have to find a way for their website to be seen and visited by users.
This also raises the question of compensation: could AI give remuneration to the websites they take the information from ? Would there be any legislation on the subject in order for businesses to still be present on search engines results ? Or would businesses have to pay AI services in order for their information to be shown first to the user in the AI summary ? If that is the case, we could also imagine the creation of businesses specialized in AI referencing. This new service could be a way for businesses to survive AI summary and the zero clicks behavior.
As the biggest AI companies are owned by Chinese or American companies, we could also question the appearance of bias in the content generated by these AI for users all around the world. Each country could own its AI in order to control the flow of information given to the user and keep a certain level of ethics according to the country.
What about Korea?
In South Korea, the dominant search engine is Naver. Often deemed as the “Google of Korea”, Naver remains the go-to search tool for millions of Korean users. As of 2025, Naver holds a significant 63% share of the Korean search market.
Since March 2025, Naver has been offering AI Briefing, a generative search module that provides summarized answers directly at the top of the search results, just like the AI summaries generated on top of Google search pages. This service is powered by Naver’s proprietary model HyperCLOVA X, alongside specialized sub-models for query analysis, summarization, and document interpretation.
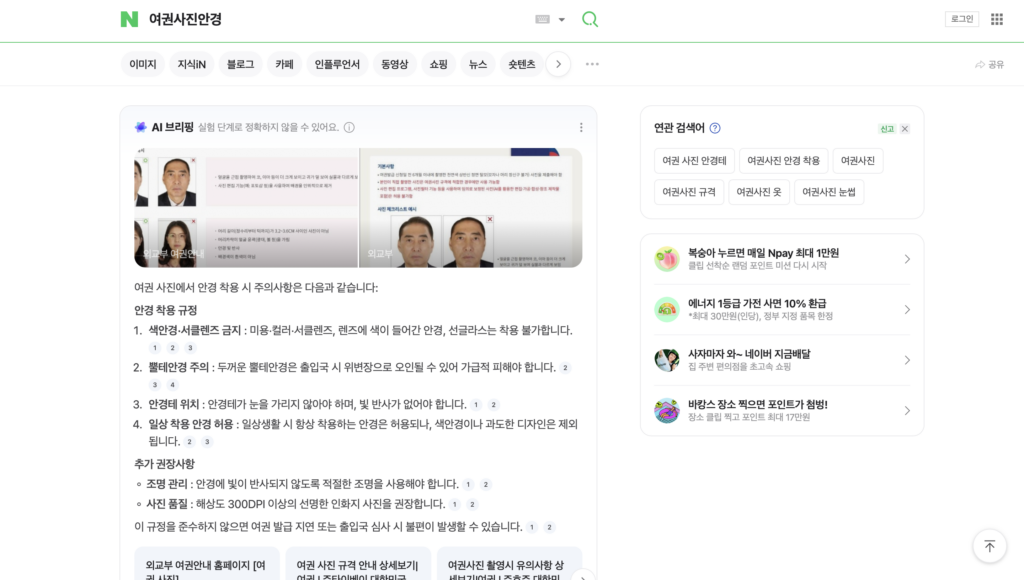
The answers are more tailored to the Korean context, unlike Google, as it activates for local topics and reflects domestic trends (e.g., dream interpretations, popular Korean dishes, frequently visited Japanese destinations by Koreans). AI Briefing also prioritizes content-related information such as summaries of popular movies and dramas in Korea. By the end of 2025, Naver plans for up to 20% of all searches to include an AI Briefing.
Naver: A closed ecosystem
Naver is a closed ecosystem that is self-sufficient. It is made of different categories related to the research. Results from a research on Naver are leading to internal websites that are not open to SEO. Here, the research is on a famous skin care product in Korea, known for its effectiveness on the skin.
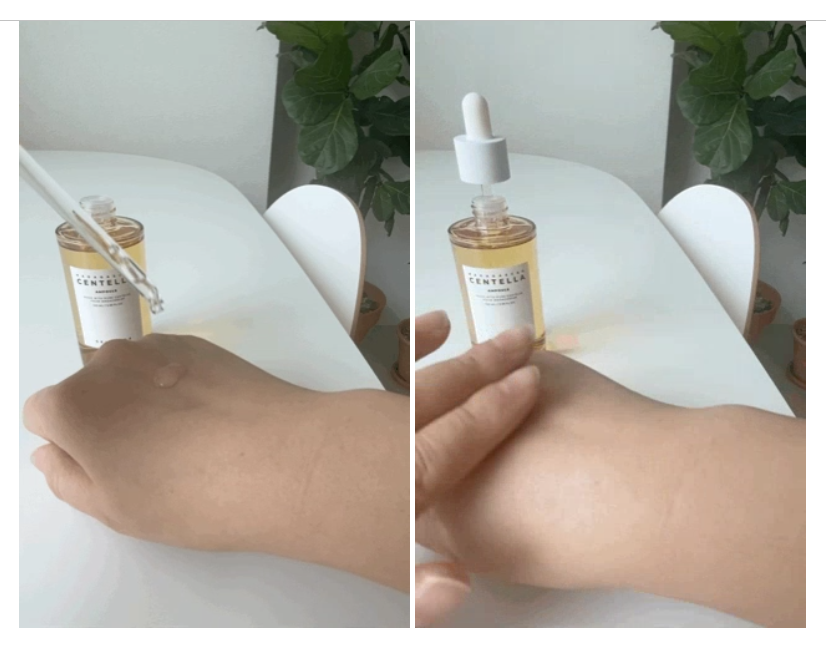
This is an example of Naver Blog (the first category), one of the most popular categories on Naver. Koreans use it very often before buying a product, in order to have reviews. In these blogs, the writer does a full review of the product, from its packaging to its use, while giving their opinion.
One of the main parts of Naver is that in order to be seen and have a community, the writer needs to produce native content that will concern Koreans. The goal of the strategy is to create content and be rewarded according to its number of views, which does not depict a traditional SEO scheme.
What does it mean for brands and agencies?
As generative AI reshapes how people search online, traditional SEO strategies are undergoing a disruption on platforms like Google. But it is far from being the case for Naver. As previously explained, Naver works as a closed ecosystem. Through its proprietary AI models HyperCLOVA X, Naver is embedding intelligent features directly into its services. It enhances how content is created, organized, and discovered without ever needing to leave the Naver environment.
This approach reflects Naver’s long-standing platform-first strategy. Rather than relying on web crawling or external site ranking, Naver’s search experience has always favored internal content: blog posts, shopping pages, Café forums, and native brand stores. Now, AI is simply making that internal ecosystem smarter, more personalized, and more efficient. The AI wave is not a threat to Naver, but rather a tool that reinforces the platform’s dominance by improving discoverability, boosting internal engagement, and encouraging users and brands to invest more deeply in the ecosystem. On Google, AI-generated results can bypass traditional SEO, causing brands to lose visibility. But on Naver, since visibility has never been purely SEO-driven, the shift is far less dramatic. Brands need to focus on creating native content inside Naver’s own platforms and understand that content, community, and commerce are all interconnected within the Naver ecosystem.
Our added value
At Asiance, we help brands navigate the unique dynamics of the Naver ecosystem by focusing on what truly drives performance: strategic, localized content and deep platform integration. With over 20 years of experience in Korea’s digital landscape, we’ve continuously adapted to Naver’s evolving models and platform shifts. Our strength lies in bridging global brand goals with the nuances of Korean digital culture, ensuring visibility, credibility, and conversion. As traditional SEO loses ground on Google, we support clients in creating native campaigns that live within Naver’s own services, whether through blog content, Smart Store optimization, or tailored advertising solutions.
Curious about our services ? Contact us at insight@asiance.com to craft innovative marketing strategies and engaging brand experiences that resonate with your audience!














